The Role of Glutathione in IV Therapy for Reducing Oxidative Stress

Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular health and combating oxidative stress. In recent years, intravenous (IV) therapy has emerged as a popular method for delivering glutathione directly into the bloodstream, enhancing its effectiveness. This article explores the significance of glutathione, its connection to oxidative stress, and the benefits of IV therapy in reducing this phenomenon.
Understanding Glutathione: An Overview
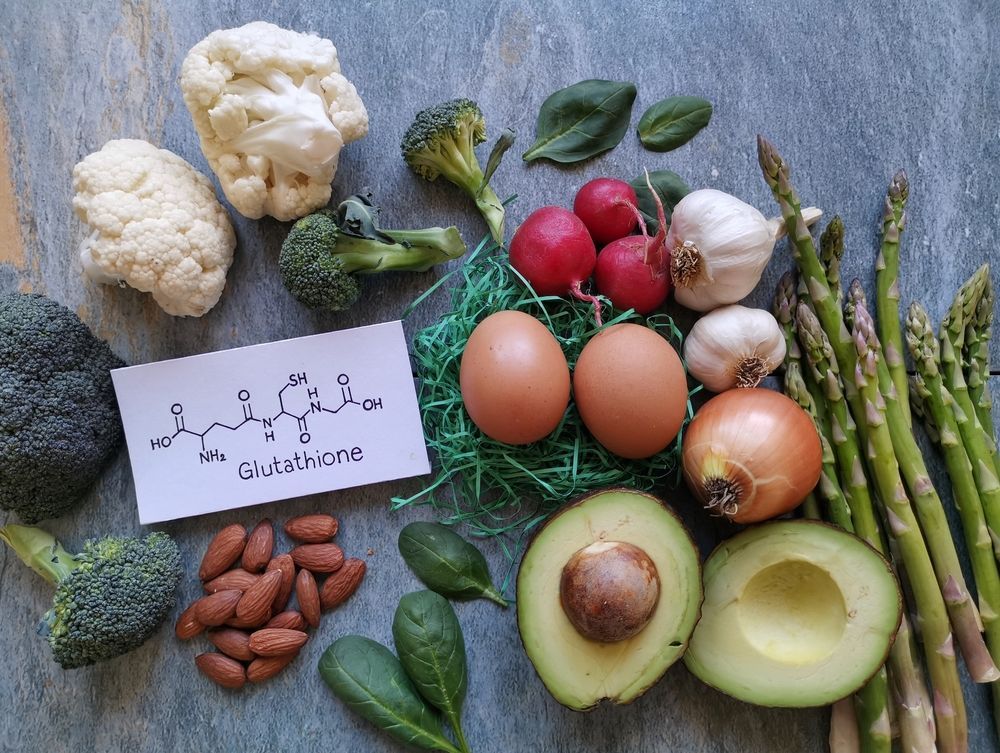
Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamine, and glycine. It is naturally produced in the body and is found in every cell, where it serves various vital functions. This small molecule is often referred to as the body's "master antioxidant" due to its ability to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
The Biological Function of Glutathione
Glutathione is critical for numerous biological functions, including:
- Detoxification: It helps in neutralizing toxins and harmful substances.
- Immune support: It enhances the function of immune cells, bolstering the body’s defenses.
- Cellular repair: It assists in repairing damaged cells and DNA.
These functions underscore its importance in overall health and well-being. Additionally, glutathione plays a role in the synthesis of proteins and the activation of enzymes, which are essential for metabolic processes. Its presence in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, is particularly noteworthy, as it helps maintain energy production and cellular health.
The Importance of Glutathione in Human Health
Adequate levels of glutathione are essential for optimal health. Low levels of this antioxidant are associated with various health issues, including chronic diseases, neurological disorders, and accelerated aging. As we age, our body’s production of glutathione declines, making it crucial to find ways to replenish it through diet, supplementation, or IV therapy. Foods rich in sulfur, such as garlic, onions, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale, can naturally boost glutathione levels. Furthermore, certain supplements, including N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and alpha-lipoic acid, have been shown to support the body’s glutathione production, making them popular choices for those looking to enhance their antioxidant defenses.
Moreover, lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management can significantly influence glutathione levels. Engaging in physical activity not only promotes the production of this vital antioxidant but also improves overall metabolic health. Conversely, chronic stress and poor dietary choices can deplete glutathione levels, highlighting the importance of a balanced lifestyle in maintaining this crucial molecule's status in the body.
The Connection between Oxidative Stress and Glutathione
Oxidative stress occurs when there’s an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to counteract their harmful effects. This condition is linked to many chronic illnesses, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Defining Oxidative Stress: Causes and Effects
Oxidative stress can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Environmental toxins: Pollution and chemicals can increase free radical production.
- Poor diet: Diets low in antioxidants can lead to oxidative stress.
- Complete lack of exercise: Sedentary lifestyles may exacerbate oxidative damage.
The effects of oxidative stress are profound, contributing to chronic inflammation and accelerated aging, making effective management essential.
How Glutathione Counteracts Oxidative Stress
Glutathione counteracts oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals, thereby reducing cellular damage. It also plays a role in regenerating other antioxidants, further enhancing the body’s defense mechanisms. By increasing glutathione levels, particularly through IV therapy, individuals can better protect themselves from the detrimental effects of oxidative stress.
Intravenous Therapy: A Closer Look
Intravenous therapy is a method of delivering fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into the bloodstream. This method is often preferred for its rapid absorption and immediate efficacy, making it particularly useful for administering antioxidants like glutathione.
The Basics of Intravenous Therapy
IV therapy involves inserting a catheter into a vein, allowing for the direct infusion of solutions. This technique is commonly used in hospitals and clinics for hydration, medication delivery, and nutrient replenishment.
The Benefits and Risks of IV Therapy
While IV therapy offers numerous benefits, such as rapid effect and higher bioavailability, it also comes with risks. Potential risks include:
- Infection at the injection site
- Allergic reactions to the infused substances
- Imbalances in electrolytes if not monitored
It's crucial for the therapy to be conducted under professional supervision to mitigate these risks effectively.
Glutathione and IV Therapy: A Powerful Combination
The combination of glutathione and IV therapy represents a holistic approach to managing oxidative stress. Administering glutathione intravenously allows for higher doses than oral supplements can provide, leading to more pronounced health benefits.
The Process of Administering Glutathione through IV Therapy
The process typically involves a health professional assessing the patient's needs and determining the appropriate dosage of glutathione. After setting up the IV line, the glutathione is slowly infused over a specified period, often accompanied by other nutrients for enhanced efficacy.
The Potential Benefits of Glutathione IV Therapy
Patients receiving glutathione IV therapy may experience various benefits, including:
- Improved skin health and complexion
- Enhanced energy levels
- Stronger immune function
- Reduction in symptoms of chronic illness
As a result, this therapy is becoming increasingly popular among individuals looking to improve their health holistically.
The Future of Glutathione in IV Therapy
The landscape of glutathione IV therapy is continuously evolving, with ongoing research exploring its full potential and mechanisms of action. Understanding how this antioxidant works at a cellular level may open up new avenues for treatment and prevention strategies.
Ongoing Research and Potential Developments
Current studies are investigating the long-term effects of glutathione IV therapy on various health outcomes, including cardiovascular health, neuroprotection, and recovery from chronic illnesses. These insights could further solidify the role of glutathione as a cornerstone in therapeutic approaches.
The Role of Glutathione IV Therapy in Holistic Health Care
As healthcare continues to shift towards a holistic model, glutathione IV therapy stands out for its multifaceted benefits. It provides an effective way to address oxidative stress, contributing to overall health and well-being. With an emphasis on prevention and personalized care, glutathione may well become a staple treatment option in the future.
In conclusion, glutathione IV therapy presents a promising solution for combating oxidative stress and enhancing health. As research progresses, its role in integrative health approaches is likely to expand, offering new hope for those striving to maintain optimal well-being.